Previous Post : What Comes After Agentic AI? Exploring the Next Leap in Autonomous Intelligence
Introduction: The Blurring Line Between Creation and Code
Defining the Focus Keyword: Generative AI Copyright
Generative AI copyright refers to the legal challenges surrounding content produced by artificial intelligence models. With tools like GPT, DALL·E, and Midjourney generating text, images, and music, the boundary between human creativity and machine output is rapidly vanishing. As AI systems become increasingly adept at mimicking human expression, the question of legal ownership becomes both urgent and complex.
The Rise of Generative AI and Its Content Creation Capabilities
Generative AI leverages vast datasets and machine learning algorithms to generate novel content. In the U.S., these tools have already been adopted across industries—media, entertainment, design, and software—enabling unprecedented productivity. However, this surge in content creation has sparked legal and ethical concerns about originality, authorship, and rightful ownership.
How Generative AI Works and Its Creative Architecture
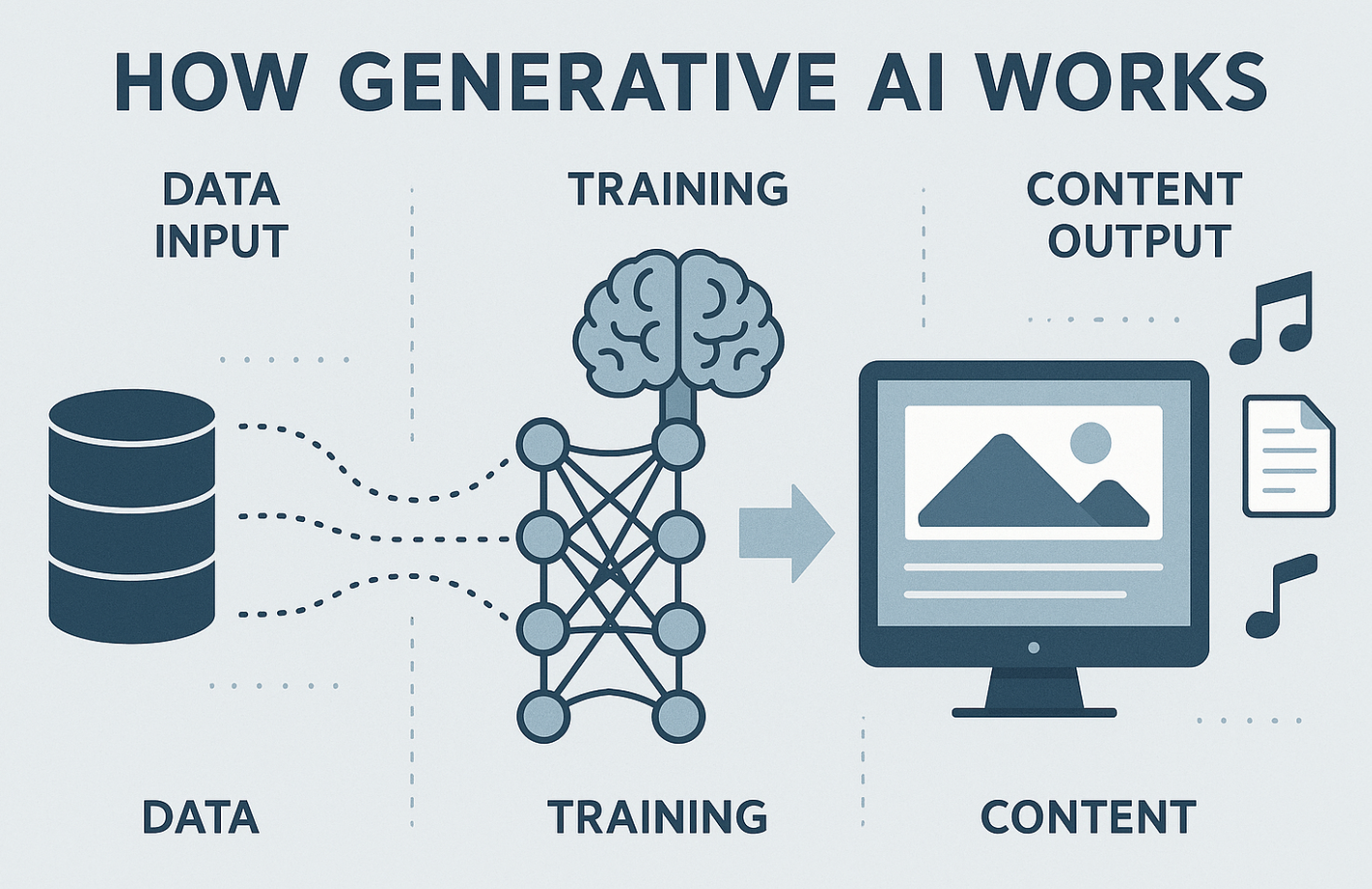
Machine Learning, Data Training, and Model Outputs
At the core of generative AI lies deep learning—a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks trained on massive datasets. These models ingest existing works, learn patterns, and synthesize outputs that resemble human-created content. In doing so, they blur the line between data reassembly and true creativity.
Assessing the Originality of AI-Generated Works
Under U.S. copyright law, originality is a key requirement for protection. However, works generated autonomously by AI raise doubts about whether they meet this criterion. Lacking a human author with creative intent, many AI-generated pieces may fall outside traditional definitions of authorship, posing challenges for registration and enforcement.
Core Issues in Generative AI Copyright Disputes

Can AI Be Recognized as an Author?
In the U.S., the Copyright Office has explicitly stated that only human beings can be considered authors under current law. This means that AI-generated content, if created without human intervention, cannot be copyrighted. However, when AI is used as a tool with substantial human guidance, copyright may still apply to the human contributor.
Determining Ownership of AI-Created Content
The issue of ownership typically centers on who contributed the creative input. In corporate environments, this may be the AI operator, the software developer, or the commissioning party. Disputes often arise over whether the user’s prompts constitute creative authorship or whether the AI platform provider retains any rights to the outputs.
The Ambiguity of Fair Use in AI Training
Fair use remains one of the most hotly debated legal doctrines in the AI space. In the U.S., courts evaluate fair use based on factors such as the purpose, amount, and transformative nature of use. Many argue that training AI on copyrighted material without permission exceeds fair use, while others contend that it is a transformative, non-commercial application that benefits society. Legal clarity is still evolving.
U.S. Copyright Law and Policy Landscape
The Copyright Office’s Stance on AI Works
In March 2023, the U.S. Copyright Office published updated guidance clarifying that works generated solely by AI are not eligible for copyright protection. Only content that exhibits sufficient human authorship can be registered. This policy was reaffirmed in key decisions rejecting AI-created artworks and novels submitted without human creative input.
Legislative Discussions and Regulatory Gaps
Although AI is advancing rapidly, U.S. copyright law has yet to be updated to address its implications comprehensively. Congress has held multiple hearings, with bipartisan interest in defining authorship, liability, and data usage rights. However, no major amendments have been enacted yet, leaving a legal vacuum around AI-generated content.
The Role of the Supreme Court and Lower Courts
While no AI-specific copyright cases have reached the U.S. Supreme Court, lower courts are increasingly grappling with issues of originality, fair use, and derivative works in the context of AI. As more disputes enter litigation, judicial interpretations are beginning to shape a de facto legal framework in lieu of formal legislation.
Case Studies: Disputes and Precedents
GitHub Copilot and the Open Source Controversy
GitHub Copilot, powered by OpenAI’s Codex, has faced backlash from developers whose open-source code was used in training without consent. A class action lawsuit filed in 2022 alleges that Copilot reproduces licensed code, violating authors’ rights. This case highlights the thin line between fair use and infringement in AI training.
Getty Images vs. Stability AI
In 2023, Getty Images sued Stability AI for allegedly using its copyrighted images to train the Stable Diffusion model without authorization. Getty argues that this not only infringes on copyrights but also devalues its licensing business. The outcome of this lawsuit could set a major precedent for how copyrighted data can be used in AI models.
Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and Artist Backlash
Both Midjourney and Stable Diffusion have been criticized for generating artworks that mimic living artists’ styles. Several artists have claimed that their works were used in training datasets without permission, prompting calls for opt-out systems and greater transparency in data collection. These cases underscore the growing tension between AI innovation and creative rights.
Creators’ Perspectives on Generative AI
Fears of Exploitation and Creative Devaluation
Writers, illustrators, and musicians are increasingly concerned that AI systems are learning from their work without credit or compensation. Many fear that AI-generated content will flood the market, reducing demand for original human-created work and diminishing the value of their creative efforts.
Strategies for Protecting Human Work
Some creators are turning to digital watermarking, blockchain copyright registration, and legal advocacy to protect their work. Others are lobbying for AI transparency laws and data usage disclosures. Industry associations are also drafting ethical guidelines to ensure fair treatment of human content in the AI ecosystem.
Tech Companies’ Responses and Industry Practices
OpenAI, Google, and Meta’s Copyright Policies
Major AI firms have begun shaping their own policies to address copyright concerns. OpenAI emphasizes responsible AI use and is working to provide more transparency around GPT’s training data. Google has implemented licensing agreements for its AI tools, while Meta is building opt-in/opt-out systems to let creators manage how their data is used.
Ethical Data Collection and Transparency
With increasing pressure from regulators and creators, tech companies are investing in better data governance. Some models are trained on publicly available or explicitly licensed datasets. Firms like Adobe claim their AI tools are “ethically trained,” assuring users that content is created with copyright-safe materials.
The Evolution of Copyright Protection Technologies
Blockchain-Based Rights Management
Blockchain is emerging as a robust tool for copyright protection. By recording proof-of-ownership and timestamping creative works, blockchain can help artists verify original creation and track unauthorized usage—particularly useful when confronting AI systems that mimic style or composition.
Digital Watermarking and AI Identification
New watermarking techniques embed invisible markers into images, music, or videos, making it easier to detect unauthorized reuse or AI-generated copies. Google’s SynthID is one such example, embedding AI-only detectable patterns in generated content to distinguish it from human work.
Licensing Models for AI-Generated Content
Creative Commons and Applicability to AI
There is ongoing debate about whether Creative Commons (CC) licenses can apply to AI-generated works. Since CC licenses require a human author to grant permissions, works produced autonomously by AI may not qualify. However, creators who use AI as a tool may license the output under CC if substantial human input is involved.
Commercial Use and Licensing Risks
Using AI-generated content commercially can pose legal risks if training data sources are unclear or unauthorized. Companies are advised to use AI models trained on “clean” datasets or purchase licenses that guarantee safe use. AI content marketplaces are beginning to offer licensed AI works with usage rights clearly defined.
International Trends and Future Outlook
Legislative Trends in Japan, Singapore, and the UK
Japan permits AI to train on copyrighted material under a flexible interpretation of fair use, supporting tech innovation. Singapore promotes AI responsibility through frameworks rather than strict regulation. The UK is considering changes to its copyright law to balance creator rights with AI development. These global approaches offer varied models for future U.S. legislation.
The Need for Global Copyright Standards
As AI platforms operate internationally, inconsistencies in copyright laws complicate enforcement. Organizations like the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) are working to establish common ground, but reaching consensus remains difficult due to differing national interests and legal traditions.
Ethical Questions and Societal Reflections
Who Bears Responsibility for AI-Generated Content?
When AI creates harmful, biased, or plagiarized content, responsibility is unclear. Developers, users, and platform providers may all share some liability. Ethical AI development requires clear accountability, human oversight, and mechanisms to correct misuse or bias in generated content.
Will AI Replace Human Creativity?
While AI can assist with repetitive or formulaic tasks, it lacks emotional depth and lived experience. Many experts believe AI will augment rather than replace human creativity. However, in industries like journalism, stock photography, and music composition, displacement is already occurring, prompting ethical and economic debates.
Industry-Specific Impacts of AI Copyright Issues
Publishing, Film, and Music
Publishing houses are using AI to generate outlines and short-form content, while the film industry employs AI for storyboarding and visual effects. In music, AI composition tools are helping creators but also raising questions about originality. Legal disputes in these sectors will likely define future norms.
Marketing and Journalism
AI tools have revolutionized digital marketing by automating content creation for blogs, ads, and SEO. However, in journalism, concerns over AI-generated misinformation and loss of editorial integrity persist. News outlets are experimenting with hybrid models that pair AI with human oversight.
Copyright Risk Management for Businesses
Legal Risk Assessment for AI Adoption
Businesses utilizing generative AI must assess potential copyright liabilities before deployment. Key considerations include the source of training data, the nature of the output, and whether the content is used commercially. Proactively consulting with legal counsel and implementing due diligence protocols can mitigate risks.
Internal Policies and Compliance Strategies
Developing internal policies on AI use is essential. Companies should establish approval workflows, documentation requirements, and clear rules about when and how AI-generated content can be published. This includes defining ownership rights and ensuring vendor contracts cover copyright responsibilities.
The Importance of Education and Awareness
Copyright Literacy for the General Public
As generative AI becomes mainstream, users must understand the legal and ethical implications of using AI-generated content. Educational campaigns, online courses, and platform-integrated warnings can help non-experts make responsible decisions and avoid infringement.
Training Developers and AI Professionals
AI developers must be educated on intellectual property laws, ethical data usage, and the legal boundaries of AI capabilities. Incorporating copyright education into computer science and machine learning curricula is becoming increasingly necessary as demand for responsible AI grows.
The Future of Technology and Legal Harmony
Balancing Innovation with Legal Structure
Technology is outpacing law, but thoughtful policy can help both coexist. Rapid innovation should be matched with flexible legal frameworks that adapt to new forms of creativity. This includes AI-specific copyright categories or expedited registration systems tailored to hybrid human-AI works.
Building a Sustainable Creative Ecosystem
To ensure generative AI supports rather than erodes creativity, a cooperative approach is needed. Stakeholders must agree on data transparency, fair compensation models, and ethical AI deployment. Only then can a balanced ecosystem emerge that empowers creators, respects legal norms, and fosters innovation.